December 12, 2022
If it looks like data and acts like data, surely that means it is data? It accrues the same rules and regulations regardless of its description and will attract fines if mismanaged or misused. As an example of ‘misuse’ look no further than the astounding Facebook/Cambridge Analytica scandal in which: “… Facebook processed the personal information of users unfairly by allowing application developers access to their information without sufficiently clear and informed consent, and allowing access even if users had not downloaded the app, but were simply ‘friends’ with people who had.”
If ever challenged by the regulators, you can assume that ignorance will be no defense if something has gone wrong. Facebook was fined £500,000 in 2018.
You comply or you don’t. It’s that simple.
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
So, why is it important for businesses and other organizations (because it is) to get a very firm handle on what the descriptions Structured, Unstructured, and Dark mean? The quick answer is that one of them sounds pretty good and two sound less so.
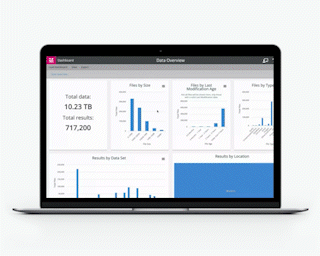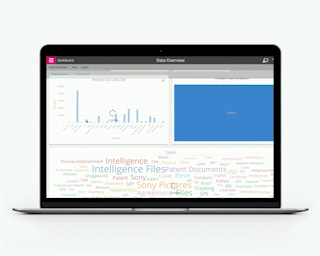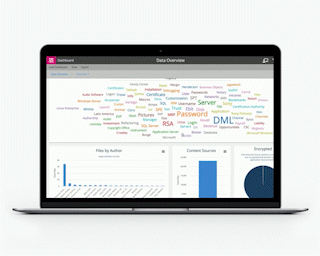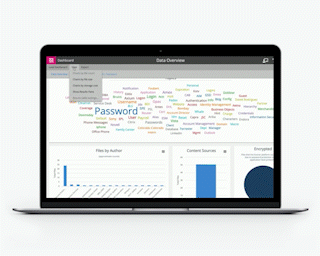
The corollary is that you have to know what your organization has, both in the data it holds and the implications that could be lurking within it.
Good suggests efficient. And efficiency suggests reliability, trustworthiness, usefulness, cost-effectiveness, and productivity; a well-spring of Business Intelligence and the underpinning foundation of confident strategic planning.
Structured Data is all those things and more. Anything less points to poor data quality management. If there’s the remotest degree of uncertainty about what or where the data is, expressing any judgment on–or modification of–its quality becomes, at least, difficult and, at most, impossible.
Here’s what they mean:
- Structured Data: This is data that has been purposefully — and rationally — gathered and captured with a view to being of value either on an ongoing basis or at some future point yet to be decided. It can be analyzed because you know where and what it is.
When you want it, you can easily, instantly, access it. It informs smart decisions, creates audit trails, and meets compliance obligations. It serves the business or organization, enabling it to better serve its customers, citizens, patients, or partners (such as supply chain participants).
- Unstructured Data: Typically, this is data that tends to be scattered around the organization, having not found a home in a database. It has not been tidily captured, filed, or labeled.
Unstructured Data might include emails, social media posts, mobile activity, basic text, sensor data (usually coming via the Internet of Things or IoT), PDF files, and mobile activity. In short, anything that has been relatively randomly generated or gathered without recourse to any sort of centralized system. It’s estimated that less than one percent of this data is used to any degree of value to an organization.
- Dark Data: This sounds like the exciting one, and it is. Gartner defines it as: “…the information assets organizations collect, process and store during regular business activities, but generally fail to use for other purposes (for example, analytics, business relationships and direct monetizing)”.
Dark Data is a Maverick, living outside the fringes of normal computer processing, so not usually analyzed for the value it holds.
That’s where the excitement is, because whether structured, unstructured, or dark, all data has value. Basically, even the ‘bad’ and ‘ugly’ can be good. The challenge is finding the data and extracting its benefits.
Leave No Data Behind
This use of the word ‘Maverick’, to describe Dark Data, is interesting. It serves to demonstrate the point about both Unstructured and Dark Data.
The dictionary definition says that a maverick is: “A person who shows independence of thought and action, especially by refusing to adhere to the policies of a group to which he or she belongs”.
Apply that thought to data and it suggests enormously high potential insight in existence in your organization today, right now, that you may simply not have leveraged. It’s sitting there, doing nothing. Yet it was generated as the result of someone, somewhere, has decided at some point that whatever their action was that generated the hard-to-find data, there was a rationale behind it.
Get Smarter
This is why the differences matter; because allowing them to clash, or lie dormant, is just clunky. It’s also lost opportunity; insight “gems”, idling in “dark unfathomed caves”
Unstructured data is unidentified, which means unsearchable in any other manner than sheer, numbing, hard work; needles and haystacks spring to mind. The information you may want, when you want it, will certainly not spring to your attention. You may not know you have it.
You may be unaware of the potential you have for improving something. If that sounds vague, it’s because you may also have no idea about what that something may be. This is a common enough scenario given that of the data that an organization handles daily, some 80 percent of it is unstructured. So, the bulk of the data is unused. It’s pretty much knowledge within the organization that the organization has no knowledge of.
What matters is accessing that knowledge and unleashing its potential. The only ‘bad’ and ‘ugly’ within your data is data that’s non-compliant. Here’s further good news–as you get to grips with the state of your data from the point of view of optimizing its value, you’ll also find out where true problems might be lingering which, in itself, is an opportunity.